As global ecommerce increases in popularity and becomes more available to a wider audience, global brands and retailers need to stay on top of trends in order to provide their customers with the best shopping experience and ultimately increase conversions.
While having a mobile-optimized website is almost a given at this stage, with 62% of US smartphone users having made an online purchase in the last 6 months – the importance of optimizing an ecommerce website cannot be overstated. However, it’s not the only technology trend to impact and improve ecommerce sites.
Based on extensive research by the Product Strategy team at ESW here are five of the most important technology trends and innovations that will affect ecommerce businesses in the coming months and years.
1. AI
AI (artificial intelligence) is a collective term for computer systems that can sense their environment, think, learn and act in response to what they are sensing and their objectives. Machine learning is an application of AI that provides systems the ability to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
Some of the ways AI is being used to improve customer experience are in fraud management, price optimization, and visual search.
- Fraud Management – Machine-learning technology can help fraud prevention teams identify fraud as it happens and stop activity before any damage can be done.
- Price optimization – Machine learning can consider a large number of products and optimize prices globally based on patterns from previous data.
- Visual search – AI can use image recognition to find similar products through uploading a photo and using AI to identify similar brands, colors, patterns and more.
However, implementing AI is not without its challenges for retailers – from data management to a lack of empathy from chatbots. Accessing the data needed for machine learning is going to be one of the biggest challenges facing developers, particularly when it comes to harvesting personal data since the implementation of GDPR.
The success of AI may be hampered by the lack of empathy or emotional intelligence in current AI solutions such as chatbots, which results in a barrier to effectively engaging with customers.
2. Blockchain
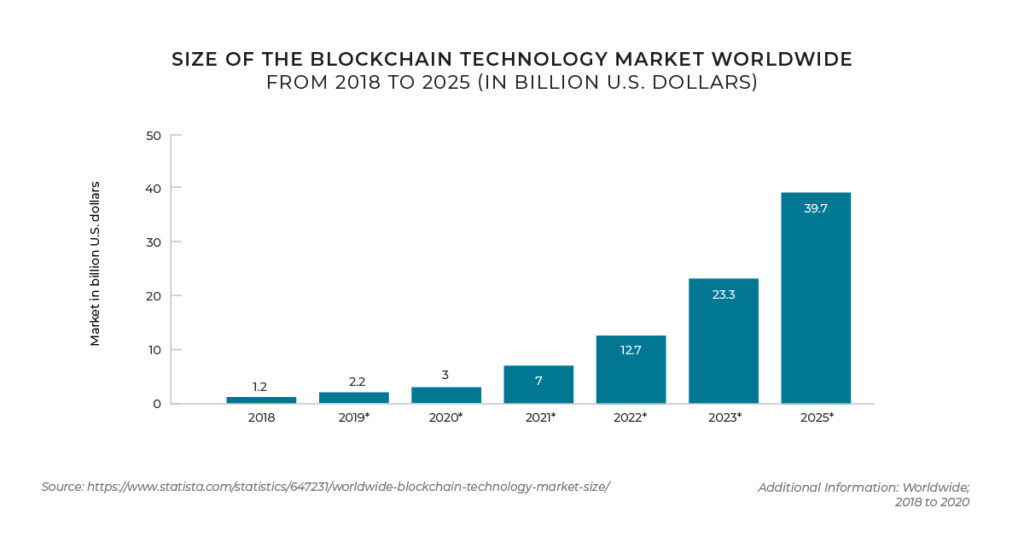
Blockchain technology is essentially a series of ‘blocks’ made up of digital pieces of information that have a number of functions. They store information about a transaction, about who’s participating in a transaction (a digital signature similar to a username), and information that distinguishes them from other blocks.
Blockchain has a lot of opportunities, such as providing an end to end supply chain solution to enable manufacturers to order, sell or trace, and pay for goods once they arrive at their destination. It can also allow customers to share their shopping history with multiple brands and therefore opens up the possibility of loyalty programs that can be used across retailers. However, there are challenges with the technology. It is often not fully understood which can lead to a lack of trust and present a barrier to adoption. Additionally, there’s a widely held perception that blockchain requires high capital investment and incurs significant operational costs. This another major barrier to mainstream adoption.
3. Online Payment Methods
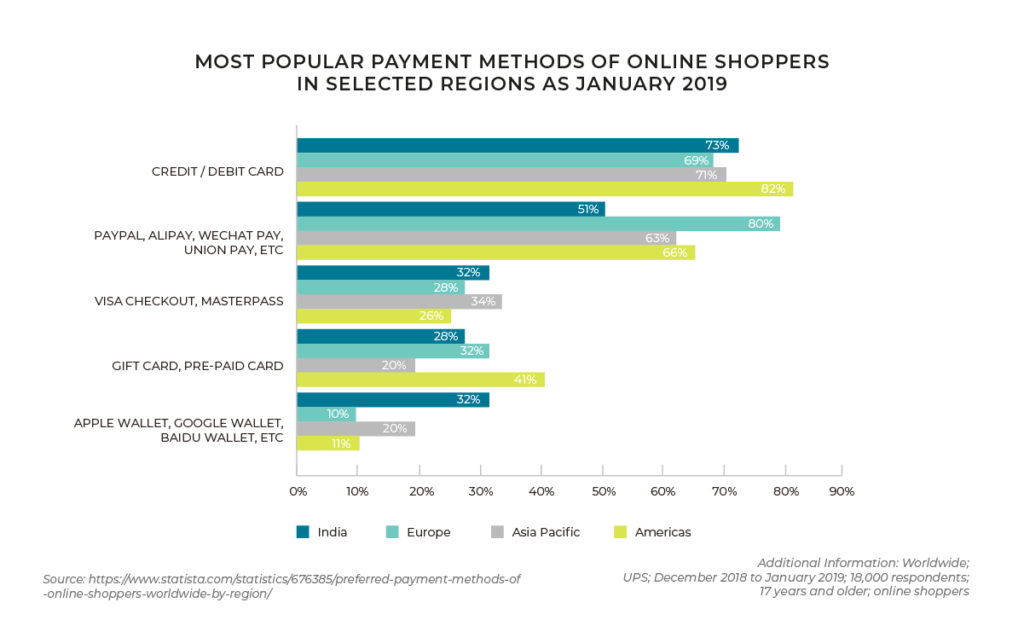
Alternative payment methods (APM) are defined as any non-card payment methods and are on the increase to meet the needs of consumers online. From ewallets to point of sale purchase financing, a number of innovations have already been implemented in the payments space with more emerging. This gives retailers the opportunity to meet a wide range of payment preferences of the shopper.
Some of the challenges presented by having a variety of payment options include being able to offer all the APMs their customers desire. It is common to use payment service providers (PSPs) which have the necessary infrastructure in place to accept APMs.
4. AR/VR
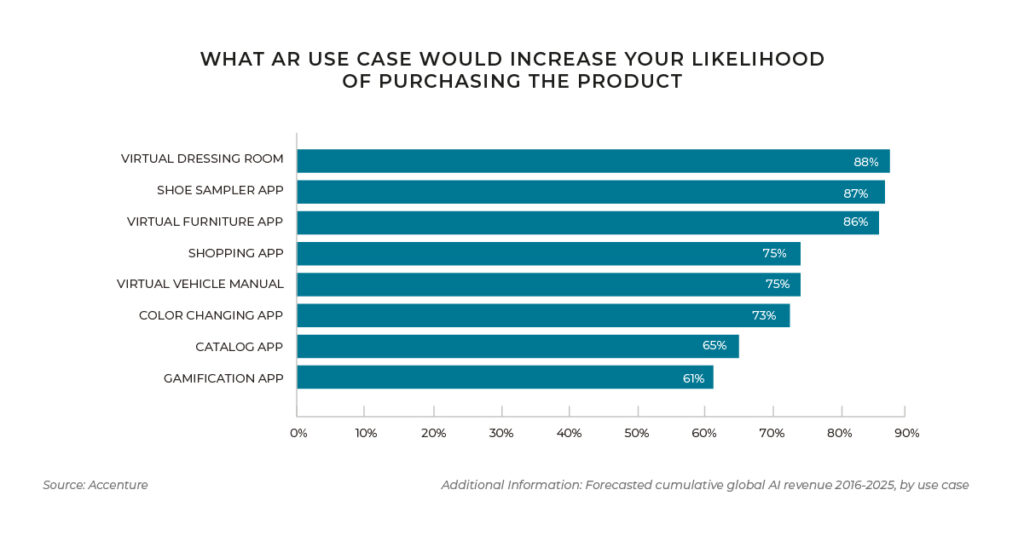
Augmented reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are being increasingly developed and implanted in the retail experience to help shoppers visualize products and ultimately increase conversions. Some brands such as Topshop, De Beers, and Converse are already using augmented reality to enable their customers to ‘try on’ clothes, jewelry or shoes, with the aim of reducing online returns.
Beauty is an industry where AR applications have already been a success. L’Oréal acquired Modiface in 2018 to help the company launch a variety of AR-powered beauty experiences across the L’Oréal brands.
Of course, with new technology, there will always be challenges from user experiences not meeting user expectations, to consumer electronics not being able to give the full experience. It is estimated that in 2019 over 2 billion smartphones will have the power to run mobile AR.
5. Voice Commerce
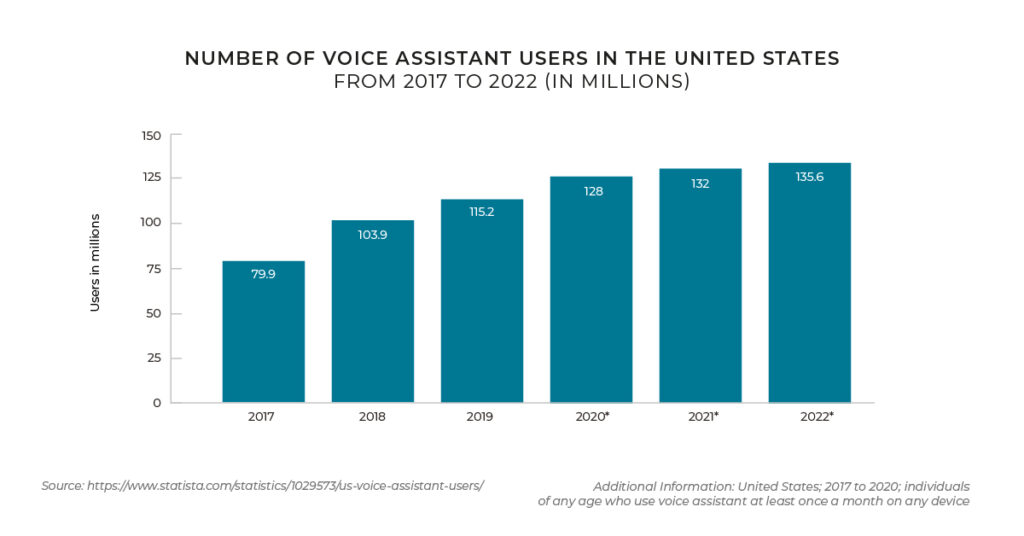
Voice commerce is the processing of voice orders by ‘voice assistants’ such as Siri and Alexa. While phones and smart speakers have had voice-activated functionality for some time, tech firms are now incorporating voice into a wider array of Internet of Things (IoT) devices such as computers, smart locks, and cars.
For retailers, there are multiple opportunities for voice commerce to help improve customers’ shopping experiences and increase conversions. From voice search, where shoppers can use their voice to search for products, to voice purchasing (which ASOS has launched on Google Assistant with its shopping bot ‘Enki’) to voice re-ordering (Alexa has this capability based on a user’s purchase history). Re-ordering by voice is popular because there is no need to see products or do a comparison shop.
Voice commerce also presents a number of challenges. There is a risk that the customer experience does not meet expectations. Retailers then run the risk of losing the ‘human touch’ in customer service due to technical limitations.
Other challenges include optimizing the channel of communication, improving voice commerce penetration and the fact that it’s difficult to incorporate voice search into an existing transactional offer.





